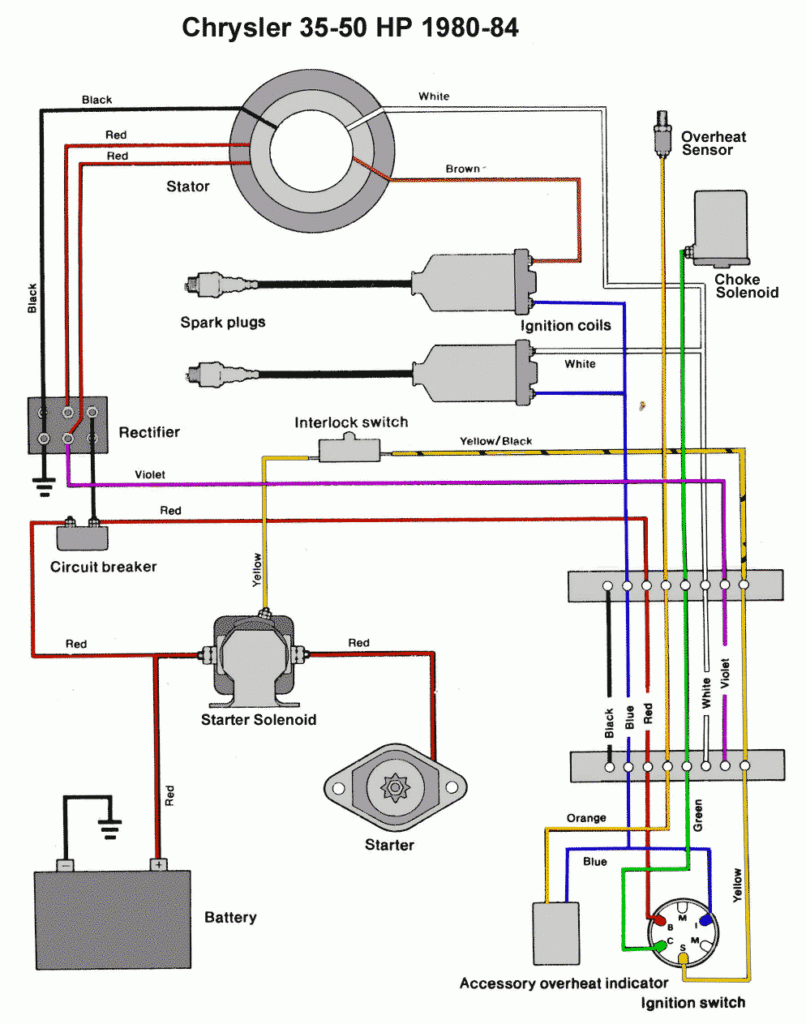
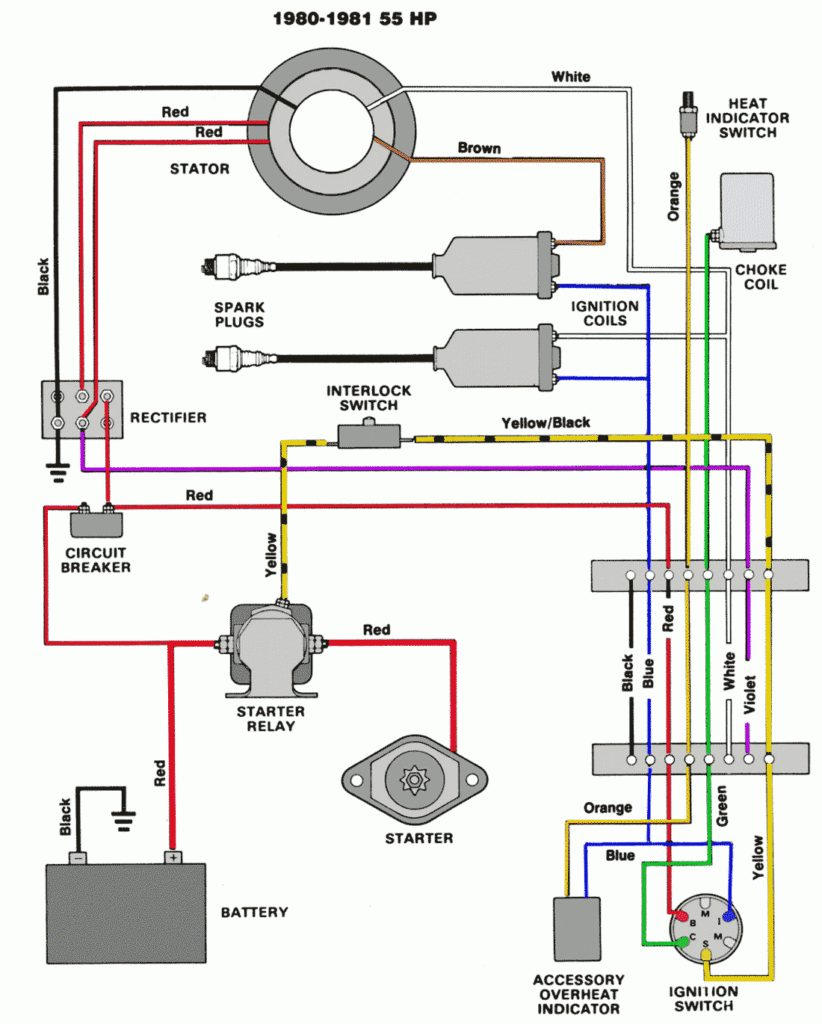
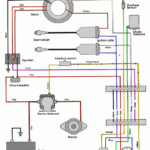
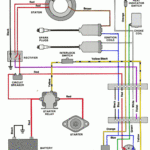
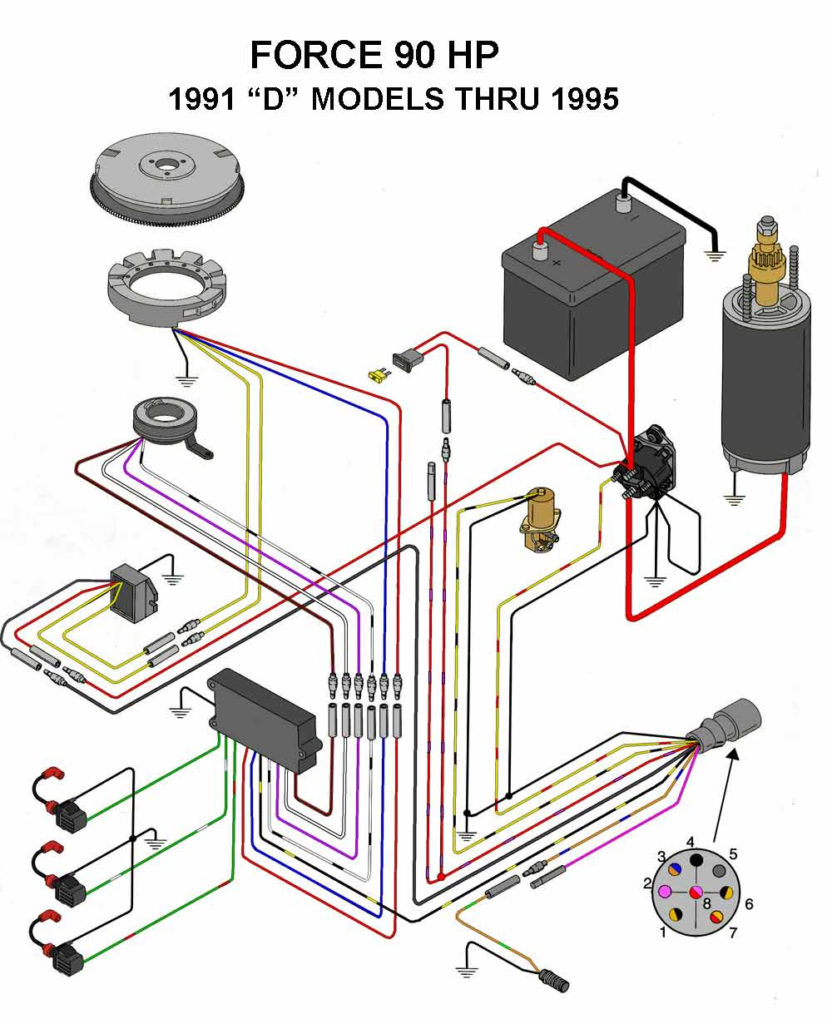
Force Outboard Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram – We will first take a look at the different kinds of terminals on the ignition switch. They include terminals for the Ignition switch, Coil, and Accessory. Once we know what these kinds of terminals are for We will then identify the different parts of the Force Outboard Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram. We will also discuss the function of the Ignition switch and Coil. Then, we’ll turn our attention to the Accessory terminals.
Terminals for the ignition switch
An ignition switch is comprised of three switches. They feed the voltage of the battery to many different places. The first switch powers the choke. The second switch controls the ON/OFF of the ignition switch. Different manufacturers utilize their own color-coding method for the various conductors, which is explained in a different article. OMC employs this system. The ignition switch comes with a connector for adding the tachometer.
Although some ignition switch terminals do not have the original design however, the numbers may not match the diagram. First, check the continuity of all wires to ensure they are correctly connected to the ignition switches. This can be accomplished using a cheap multimeter. After you’re sure that all wires are running in good harmony then you can connect the new connector. The wiring loom used in the ignition system switch supplied by the manufacturer is different.
Understanding how ACC outputs are connected to the auxiliary outputs of your car is vital. The ACC terminals and IGN terminals function as the primary connections to your ignition switch. The START and IGN connections are the most important connections for stereo and radio. The ignition switch’s function is for turning the car’s engine on and off. The terminals for the ignition switch on older vehicles are marked with the letters “ACC” and “ST” (for individual magneto wires).
Terminals for coil
The first step in determining the kind of ignition coil is to know the terminology used. The basic ignition wiring diagram illustrates a variety of connections and terminals. There are two primary and one secondary. Each coil comes with its own operating voltage. To determine which type of coil you have first, you need to determine the voltage at the S1 primary terminal. S1 should be checked for resistance to identify if the coil is Type A, B, and/or C.
The chassis’ negative needs to be connected to the low-tension side. This is also the ground in an ignition wiring diagram. The high-tension side supplies positive direct to the sparkplugs. The coil’s aluminum body needs to be linked to the chassis for suppression but isn’t required. The ignition wiring diagram will also show you the connection of the negative and positive coil’s terminals. In certain cases, a scan at your local auto parts store can help you identify the malfunctioning ignition coils.
The black-and-white-striped wire from the harness goes to the negative terminal. The negative terminal is served by the black trace that’s joined to the white wire. The contact breaker is connected to the black wire. To check the connections between the two wires, employ a paperclip to lift them out of the housing. Be sure to ensure that the terminals haven’t been bent.
Accessory terminals
The wiring diagrams of the ignition illustrate the different wires used to provide power to the various parts of the car. There are generally four color-coded terminals to each component. Red refers to accessories, yellow to the battery and green the starter solenoid. The “IGN terminal” is used to provide power to the wipers as well as other operating features. The diagram shows how to connect the ACC and ST terminals to the other components.
The terminal referred to as BAT is the location where the battery is. The electrical system will not start when the battery isn’t connected. Additionally, the switch will not be able to turn on without the battery. If you’re not sure of where your car’s battery is situated, look at your wiring diagram to see where it is. The accessory terminals of your car are connected to the battery and the ignition button. The BAT connector connects to your battery.
Some ignition switches come with an additional position. This lets users connect their outputs to a different place without the ignition. Sometimes, customers want to utilize an additional output that is not connected to the ignition. Use the additional output by connecting the connector to an ACC terminal on your switch with the same colors. This feature is convenient however it does have one key distinction. Many ignition switches have an ACC position when the car is in ACC mode and a START mode when it is in IGN.